Webinar Recap: Delivering Live Video in Challenging Network Environments
Global organizations rely on video communications to connect their dispersed workforces but providing a high-quality digital experience to every employee no matter their location is a challenge faced by many multinational enterprises operating in APAC countries. Legislative technologies like the Great Firewall of China, poor bandwidth and latency issues can be disruptive and prohibitive to delivering enterprise video at scale.
During our webinar Delivering Live Video in Challenging Network Environments , Stephanie Newman, Director of Channel and Alliances EMEA at Kollective, was joined by Luca Licata, Director of Technology and Engineering at wtv. and Garrick Ransome, Technical Director APAC at Kollective to discuss trends, challenges and possible solutions when delivering global video communications.
The Growing Demand for Video at Scale
From live event webcasting to day-to-day video conferencing, video has become standard practice in the enterprise. 2020 saw, on average, a 45% growth in live video usage, according to a recent IDG Market Pulse Survey and Luca Licata pointed out that utilization of wtv. EasyWebcast jumped from 950,000 visitors to 1.5 million during this time.
The use of video has allowed international workforces to communicate and collaborate in real-time. This, alongside initiatives like the Shanghai Free Trade Zone, has led many corporations to open up in China. As part of the Kollective APAC team Garrick Ransome has seen the ability to engage with employees in China become an “essential requirement” for many global organizations.
The challenges of engaging a dispersed global workforce
Video is a bandwidth intensive application and even in the best of circumstances can put a significant strain on the network. Low bandwidth and slow technology adoption in APAC are common challenges Garrick Ransome has faced working with customers in the region. To support video, IT often has to make compromises like reducing the quality of the video or, as Luca Licata experienced, splitting a webcast into multiple sections for each department.
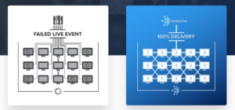
China presents its own unique challenges due to infrastructure and legislative technologies. The Great Firewall of China negatively affects live streaming due to added latency, packet loss and congestion. Video applications that don’t have infrastructure located in China require users to pull streams from outside the country leading to an inconsistent experience, disconnects or failed delivery.
Engaging Employees Effectively with Video
The shift to video has been a challenge many networks have not been prepared for. While there is always the option of purchasing additional hardware and making costly upgrades Luca Licata and Garrick Ransome shared alternatives that organizations can quickly adopt to ensure quality video delivery in challenging environments.
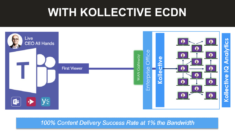
Using platforms with infrastructure located in China, like wtv. EasyWebcast, bypasses the Great Firewall, Luca Licata said, and allows viewers to pull the stream from a nearby content delivery network point of presence (CDN PoP). He went on to add that the use of a China-based CDN will help reduce latency, but as employees begin returning to the office and pulling video simultaneously, network bottlenecking becomes an issue. To avoid this, he recommends adding an enterprise content delivery network (ECDN) to optimize the network for video delivery at scale. Kollective’s ECDN uses smart peering technology to distribute content efficiently and reduces up to 99% of bandwidth consumption.

How to deliver live video events in china
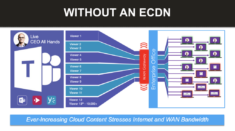
Many enterprises rely on a multi-tool strategy for communications and some of those platforms do not have infrastructure inside of China. Garrick Ransome brought up the example of Microsoft Teams and Stream which do not have local CDN PoPs and yet are heavily adopted by global organizations. He detailed two scenarios to use these applications in China:
- Bypass the Great Firewall by routing through wide area network (WAN)
- Go through the Great Firewall
In the first scenario, what can deter organizations from using this is the cost of the WAN links. For this solution to be viable for video at scale, traffic must be reduced. In this situation he recommends using Kollective’s Browser-Based Peering to:
- Lower transit costs
- Optimize network performance
- Reduce bandwidth consumption
Scenario two comes into play for many companies that do not have the infrastructure to route through WAN or their corporate policy mandates they connect through the Great Firewall. Going through the Great Firewall means added latency, unpredictable packet loss and congestion which can lead to a poor experience or event failure. This scenario requires the use of a latency tolerant solution like Kollective Agent to:
- Provide persistent caching
- Communicate over a latency tolerant UDP-based protocol
- Add an extra buffer to help recover packet loss
speak with an expert on enterprise video delivery
If you’re having difficulties delivering live video in challenging network environments, Kollective can help. Speak with an expert today to learn more about the solutions available to you.
The post Webinar Recap: Delivering Live Video in Challenging Network Environments appeared first on Kollective Technology .